Wire gauge of a brush determines the type of surface finishing:
Selection of the right type of brush
Wire type, diameter and length
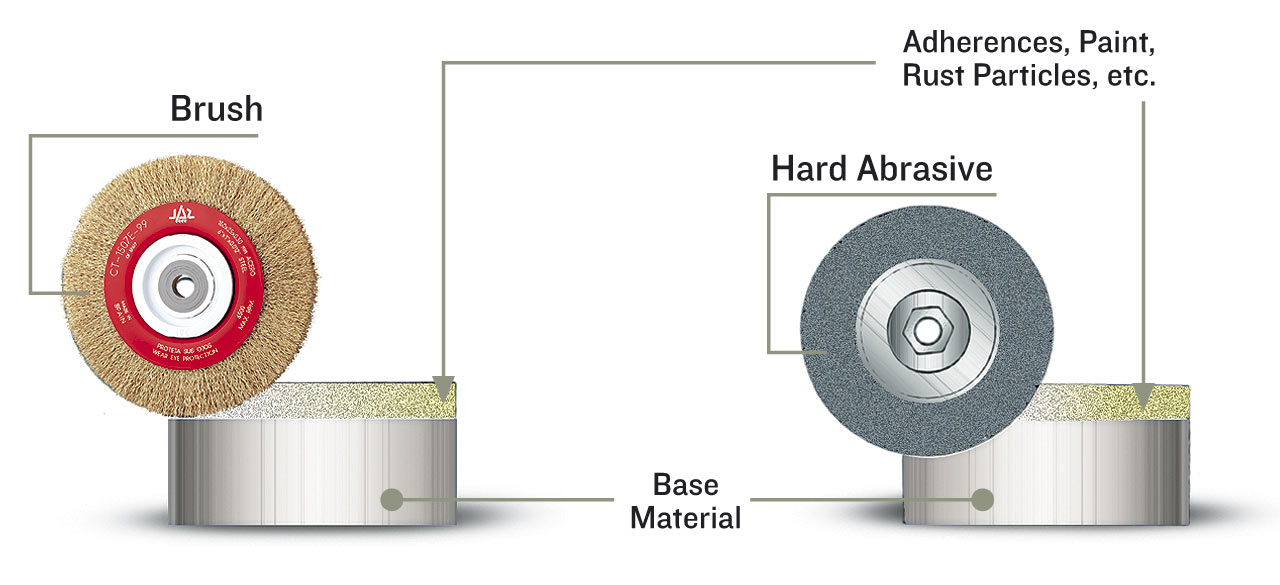
Wire Brushes Vs. Hard Abrasives
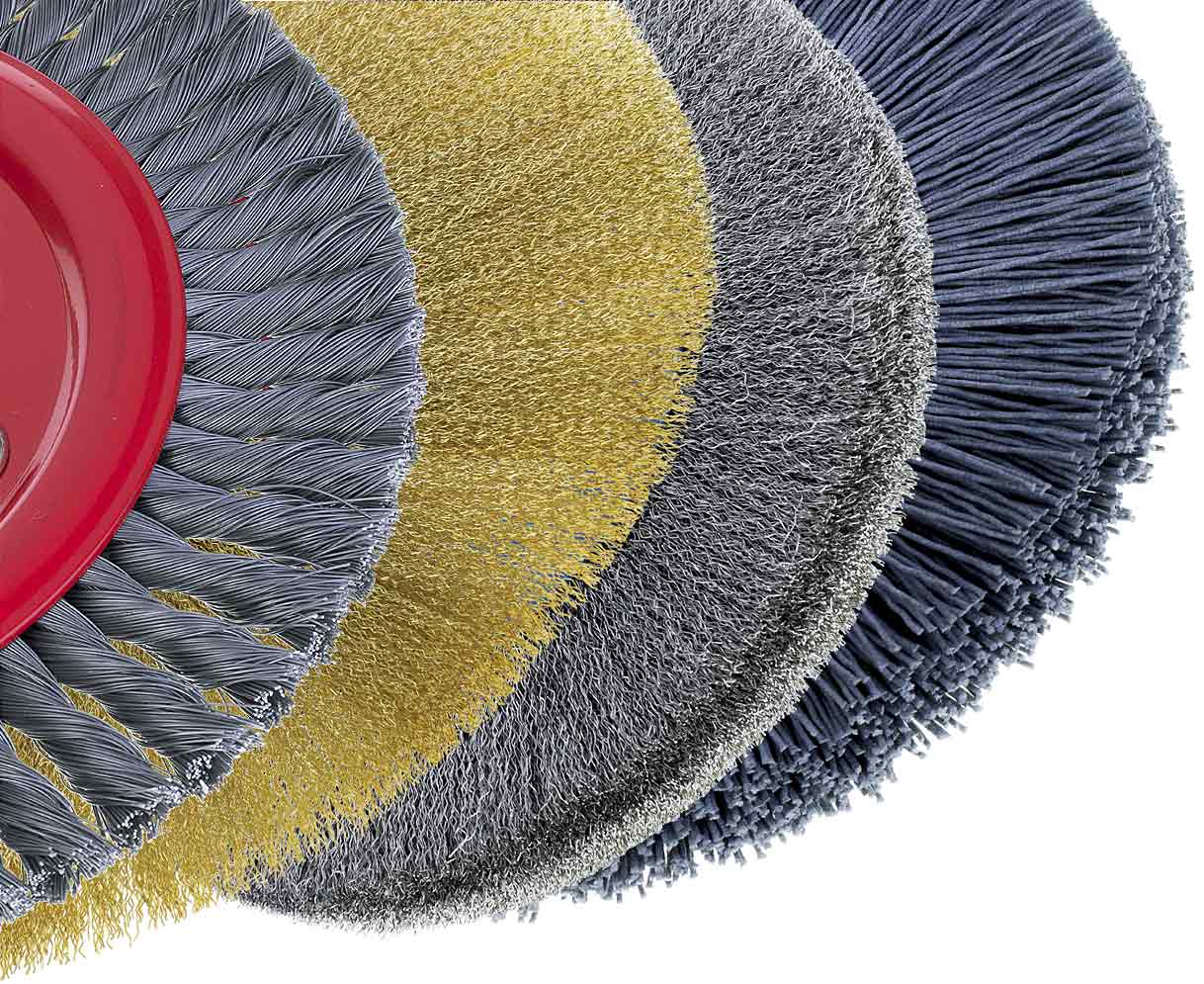

Crimped Wire, Twisted Knot Wire and Abrasive Nylon
Trim Length
Wire Diameter and Characteristics of Abrasive Nylon
Brush dimensions and R.P.M.

R.P.M.
Peripherical speed
The power tool speed influences the performance of the brush and the safety of the operador. If load speed marked on the power tool is higher than the brush MAXIMUM RPM, do not mount the brush. Maximum RPM are indicated on brush side plates and shall never be exceeded.
MAXIMUM RPM are the maximum RPM at which the brush could be run with no work applied (spinning free). It is merely a safety indication for the user, not the recommended operating speed.
Cutting speed [m/s]
| Removal | Steel | Stainless Steel and Brass | Nylon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burr | 25-35m/s | 20-25m/s | 15-20m/s |
| Weld pass | 40-45m/s | 35-35m/s | |
| Oxides, Varnishes, Corrosion | 30-35m/s | 20-25m/s | 15-20m/s |
| Paints and Scales | 40-45m/s | 35-35m/s |
Converting m/sec in ft/min: 1 m/sec = 197 ft/min | 1ft/min = 5,08 m/sec
| n | Ø Brush d1 [mm] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [r.p.m.] | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 80 | 100 | 115 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 | 300 |
| 1.000 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 16 |
| 1.250 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 16 | 20 |
| 1.500 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 24 |
| 1.750 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 23 | 27 |
| 2.000 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 16 | 18 | 21 | 26 | 31 |
| 2.500 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 33 | 39 |
| 3.000 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 27 | 31 | 39 | 47 |
| 3.500 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 23 | 27 | 32 | 37 | 46 | 55 |
| 4.000 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 21 | 24 | 26 | 31 | 37 | 42 | 52 | 63 |
| 4.500 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 18 | 19 | 24 | 27 | 29 | 35 | 41 | 47 | 59 | 71 |
| 5.000 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 20 | 21 | 26 | 30 | 33 | 39 | 46 | 52 | 65 | 79 |
| 5.500 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 17 | 22 | 23 | 29 | 33 | 36 | 43 | 50 | 58 | 72 | |
| 6.000 | 8 | 9 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 24 | 25 | 31 | 36 | 39 | 47 | 55 | 63 | 79 | |
| 6.500 | 9 | 10 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 26 | 27 | 34 | 39 | 43 | 51 | 60 | 68 | ||
| 7.000 | 9 | 11 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 27 | 29 | 37 | 42 | 46 | 55 | 64 | 73 | ||
| 7.500 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 29 | 31 | 39 | 45 | 49 | 59 | 69 | 79 | ||
| 8.000 | 10 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 31 | 34 | 42 | 48 | 52 | 63 | 73 | |||
| 10.000 | 13 | 16 | 21 | 26 | 31 | 39 | 42 | 52 | 60 | 65 | 79 | ||||
| 12.000 | 16 | 19 | 25 | 31 | 38 | 47 | 50 | 63 | 72 | 79 | |||||
| 14.000 | 18 | 22 | 29 | 37 | 44 | 55 | 59 | 73 | |||||||
| 16.000 | 21 | 25 | 34 | 42 | 50 | 63 | 67 | ||||||||
| 20.000 | 26 | 31 | 42 | 52 | 63 | 79 | |||||||||
| 22.000 | 29 | 35 | 46 | 58 | 69 | ||||||||||
| 25.000 | 33 | 39 | 52 | 65 | 79 | ||||||||||
| Material | Ø mm | Ø " | Wire Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grey Steel | 0,12 | .005 | A |
| Brass Coated Steel | 0,15 | 006 | B |
| 0,20 | .008 | C | |
| 0,25 | .010 | D | |
| 0,30 | .012 | E | |
| 0,35 | .014 | F | |
| 0,40 | .016 | G | |
| 0,50 | .020 | H | |
| 12 x 0,23 (2) | 12 x .009 | # | |
| 6 x 0,353 + 3 x 0,20 | 6 x 014 + 3 x.008 | @ | |
| Stainless Steel | 0,15 | .006 | M |
| 0,20 | .008 | N | |
| 0,30 | .012 | Z | |
| 0,40 | .016 | P | |
| 0,50 | .020 | Q | |
| 7 x 0,35 | 7 x .013 | @Z | |
| Brass | 0,08 | .003 | U |
| 0,30 | .012 | V | |
| 0,40 | .016 | X | |
| Grey Steel | 0,37 | .015 | J |
| 0,50 | .020 | K | |
| 0,80 | .032 | L | |
| German Silver | 0,08 | .003 | O |
| Flat Steel | 0,90 x 0,50 | .035 x .020 | T |
| Galvanised Steel | 0,43 | .017 | S |
| Laminated Wire | 3 x 0,20 + 6 x 0,35 | 3 x .008 + 6 x .014 | W |
| 0,50 | .020 | Y |
Example
Brush diameter d1=150mm
R.P.M.: 3000 r.p.m
Cutting Speed: 24m/s
R.P.M.: 5.000 r.p.m.
| Conversion Table mm / " | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ø Brush | Ø Wire | |||
| mm | " | mm | " | I.S.W.G |
| 25 | 1" | 0,08 | 0,003" | 44 |
| 50,8 | 2" | 0,1 | 0,004" | 42 |
| 76,2 | 3" | 0,12 | 0,005" | 40 |
| 101,6 | 4" | 0,15 | 0,006" | 38 |
| 127 | 5" | 0,2 | 0,008" | 36 |
| 152,4 | 6" | 0,25 | 0,01" | 33 |
| 177,8 | 7" | 0,3 | 0,0118" | 31 |
| 203,2 | 8" | 0,35 | 0,0138" | 29 |
| 228,6 | 9" | 0,4 | 0,016" | 27 |
| 254 | 10" | 0,5 | 0,02" | 25 |
| 279,4 | 11" | 0,8 | 0,0315" | 21 |

Main actions to be taken with brushes
Deburring
Deburring is the action of removing burrs, these are normally produced after performing cutting or machining operations on certain materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, etc.
Surface preparation
Surface preparation is the process of changing the surfaces appearance of a material. Wood is a typical material to apply this process. By passing a steel brush over a wooden surface we are able to highlight the hardest grain, replicating an aged wood look. This process is also known by the term “Rustic”.
The diameter of the wire is important to obtain the desired finish, some woods are harder and require a larger wire diameter than soft woods.
For the final step during finishing, some experts use abrasive nylon brushes, these soften the aggressive passage of the steel.
Other materials/surfaces are also prepped, such as stainless steel, stone or rubber. Preparing stainless steel is also known as a “satin finish”. A wide range of products are used to provide a satin stainless-steel finish, the most common is abrasive wheels, but in some cases abrasive nylon brushes are used, fixed to a wheel sander machine.
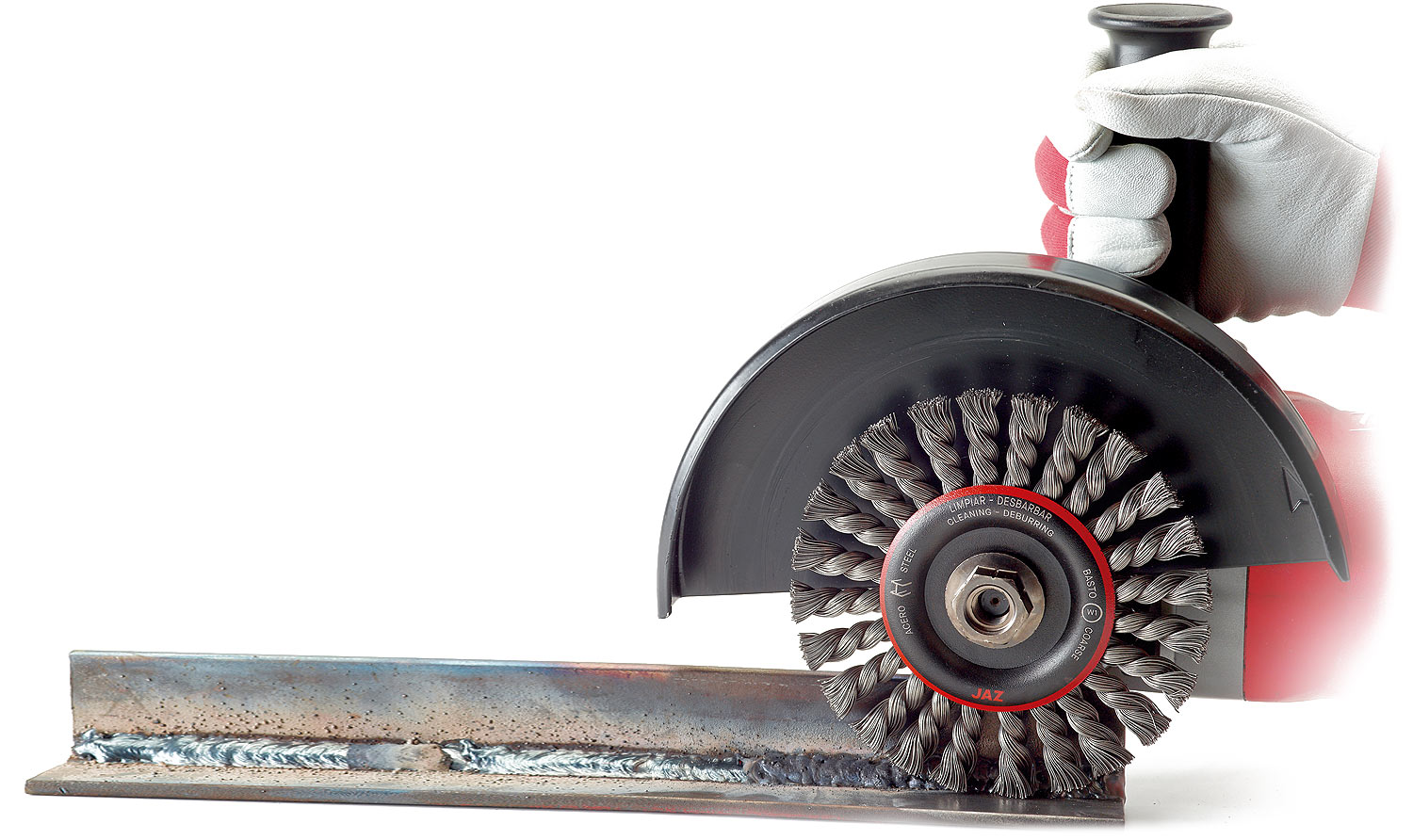
Grinding
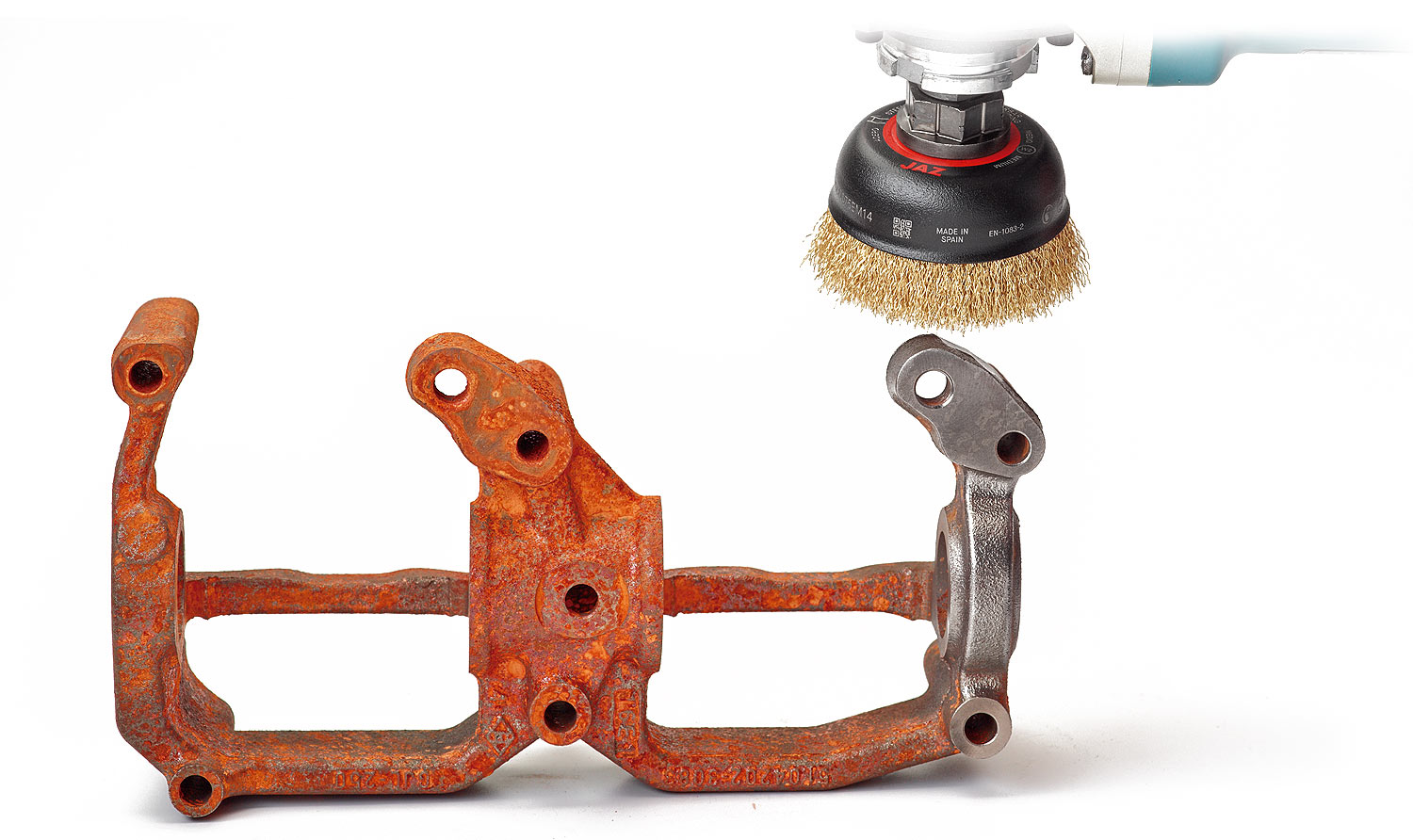
Removal of paint, rust, dirt, coatings on metal parts etc … The steel wire brush is the ideal tool for this application. The wires remove rust, paint, coatings etc … very easily.
In any of the styles of a brush, cup, circular, end brush etc … the performance is ideal for this application. If the result is not as expected, try using a larger diameter wire or changing from a crimped wire style brush to a twisted knot wire brush for more cutting action.
Cleaning
Removing of labels, cleaning of welding joints, stripping of wire rod, cleaning of molds, foundry dust, pad printing on metal parts, conveyor belts, etc …
Steel brushes are not always the right solution. Depending on the metal part to be cleaned, you can also use synthetic fibers (nylon, polypropylene, pekalon, etc.) for cleaning. For example, a plastic conveyor belt cannot be cleaned with wire brushes, but you can do it with synthetic fiber brushes.
There are other types of brushes made with natural fibers such as Horse hair, Tampico, Wild pig hair, etc.). This type of fiber has the advantage of not creating static electricity. In some cleaning processes, the friction of synthetic fibers with surfaces generates static electricity and they are useless, hence the use of vegetable fibers.
Sweeping
Eliminate melt sands, dust, flours, etc. Synthetic fiber brushes are the most suitable for this type of aplication. Normally it is about removing substances that are loosely attached to the surface.
The food industry is a common user of this type of application.
Finishing
With our main focus of finishing surfaces with the use power and hand brushes, we specialize in fill materials that can be used in brushes. With brushes it is not possible to achieve finishing that is possible with other materials such as scotch brite, abrasive sponges, etc …
In the market, abrasive nylon, aluminum oxide, diamond, etc. fibers are available. They are the most widely used abrasives in brushes. With this type of brushes, fine burrs and improvements in surface finishing are achieved. These are synthetic fiber filaments impregnated in the different types of abrasive mentioned above. The most widely used fiber is Abrasive Nylon.
| Finishing | Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire | Abrasive nylon | Sandpaper | Polish | Sweep | |
| Coarse | W1 | NA1 | SP1 | P1 | SW1 |
| Medium | W2 | NA2 | SP2 | P2 | SW2 |
| Fine | W3 | NA3 | SP3 | P3 | SW3 |
| Superfine | W4 | NA4 | SP4 | P4 | SW4 |
| Neutral | W5 | NA5 | SP5 | P5 | SW5 |
Removal
Flexibility

Surface treatment
The first step is to identify the type of surface that the application will be performed on; steel, stainless steel, aluminum, wood etc. The following is a our recommendation for what brush fill material is best to be used for each work surface material.
Carbon steel
For brushing carbon steel material, the most common brushes to use are made with carbon steel wires. Only in cases where carbon steel is at high temperatures is it recommended to use stainless steel brushes. Carbon steel rusts in heat and stainless does not.
Stainless steel
As a general rule, it is recommended to use stainless steel wire brushes for brushing stainless steel surfaces, to avoid oxidation problems in on the material.
Wood
Wood has different characteristics than other materials. The end user is the one who knows the finishing type he is looking for and that can change the criteria when selecting brushes. They are generally carbon steel brushes along with abrasive nylon brushes. The choice of wire thickness will depend on the type of wood (hard or soft), as well as the grain of the abrasive nylon.
Non-sparking
We consider Non-Sparking those metallic surfaces where sparks should not be generated when brushing because they are in environments with a risk of explosion. For brushing surfaces and not wanting to generate sparks, we recommend using solid brass wire brushes.
Other surfaces

Necessary steps for the correct choice of a brush
The choice of a brush depends on several criteria to take into account
1.
Material you are working on/ Surface to be treated
Steel
Stainless / Aluminum
Non-sparking
Wood
Others
2.
Power tool being used
Drill
Grinder
Mini-Grinder
Die-Grinder
Wood Portable Machine
Bench-Grinder
Industrial Machine
Burnishing
By hand
3.
Type of application
Cleaning
Surface preparation
Deburring
Grinding
Finishing
Polishing
Sweeping
4.
Surface finish required
| Finishing | Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire | Abrasive nylon | Sandpaper | Polish | Sweep | |
| Coarse | W1 | NA1 | SP1 | P1 | SW1 |
| Medium | W2 | NA2 | SP2 | P2 | SW2 |
| Fine | W3 | NA3 | SP3 | P3 | SW3 |
| Superfine | W4 | NA4 | SP4 | P4 | SW4 |
| Neutral | W5 | NA5 | SP5 | P5 | SW5 |
Removal
Flexibility
Work efficiency increases as a brush diameter increases. To calculate the biggest possible diameter, it is necessary to consider the maximum RPM of the power tool or machine being used (i.e. for an electric tool with maximum RPM of 6,000, the brush should not exceed 175 mm diameter).
A shorter trim length provides a more aggressive brushing action, whereas flexibility to adapt to irregular or uneven surfaces increases as trim length increases. In contrast to abrasives and cutting tools, wire brushes do not remove the base material of a treated surface. Herein, brushes serve as an essential tool for a wide range of industrial processes.
Multithreads and Adapters: The exclusive and patented JAZ threaded nut provides for a number of advantages: Easier tightening into machines. Higher resistance of the brush against possible deformation. The multithread option allows the use of one brush on machines with different types of spindle: R88 threaded nut: fits both 5/8-11” and M14-2 machines. R77 threaded nut: fits both M10x1,25 and M10x1,5.
The purpose of these innovations is to help distributors better manage the line by reducing the number of SKU-s or items and improve their level of service to their customers and end users.
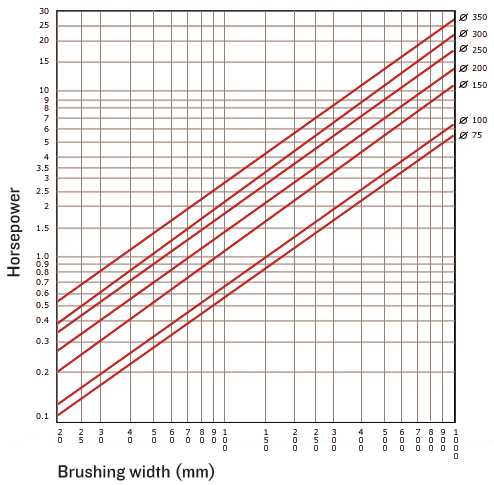
Diagram to calculate the Power required on Wheel Brushes
Contact us and tell us how we can help you
Consult us if you want to have more information related to our services or you want us to advise you about how they can fit to your firm´s needs.